

“The strength of the team is each individual member. The strength of each member is the team.”
– Phil Jackson
In today’s world, warehouse automation is not just about isolated systems performing singular tasks. It’s about the power of collaboration, where diverse entities — humans, robots, and software platforms — work together to fulfill orders. By 2027, 3/4 companies will be using robotic automation in warehouses. To achieve seamless integration and coordination among these various systems, we turn to multiagent orchestration (MAO), a revolutionary approach to problem-solving and task management.
MAO is the management of heterogeneous fleets of robots and other agents in the warehouse (like doors, elevators and even people) through software. This includes the orchestration and assignment of work while monitoring and coordinating the activities of said agents. MAO continuously optimizes fulfillment performance in real-time: the right order, with the right bot and/or agent, taking the right path and action, at the right time.
In its Hype Cycle for Supply Chain Execution Technologies, 2023, Gartner indicated that MAO platforms are “on the rise” as industries look for a way to make use of diverse fleets of robots without the need for complicated integration work.
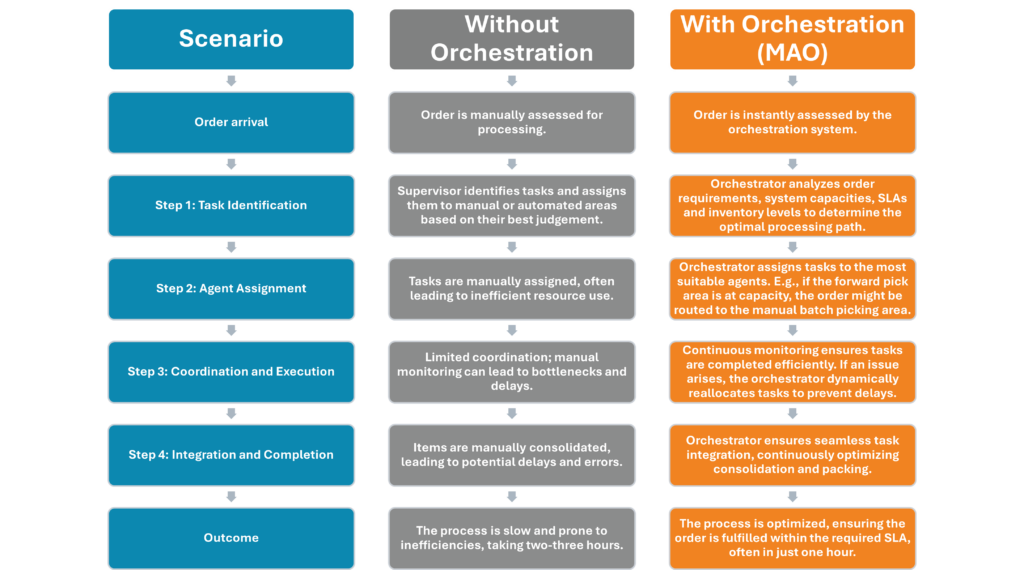
Let’s explore how an MAO platform would handle an order fulfillment scenario vs. how a traditional system would handle it.
Manual Area: Users perform batch picking, then send items to an automated sorter. Once items are sorted, the order is consolidated and sent for packing. This process typically takes 2-3 hours.
Forward Pick Area: Orders are picked directly into the packing box and processed within one hour.
Considerations:
Related Watch: How a multiagent orchestration platform works
The following components are essential for MAO-based environments.
This blog aims to simplify the complex mechanisms of MAO and highlight the human element, helping to demystify how multiple agents work together in real life to achieve the best possible results.
If you’d like to delve deeper into MAO, check out our whitepaper: Multiagent Orchestration, Explained. And if you’re interested in seeing how MAO would work in your automation environment or exploring the specific tasks that can be automated and optimized, contact us for a custom demo.